Categorised under:
Interventional Radiology
>
Oncology
>
Microwave ablation
The new Emprint Microwave ablation system from Covidien/Medtronic is an advance in microwave technology. The company have used various techniques in an attempt to produce a more spherical ablation zone.
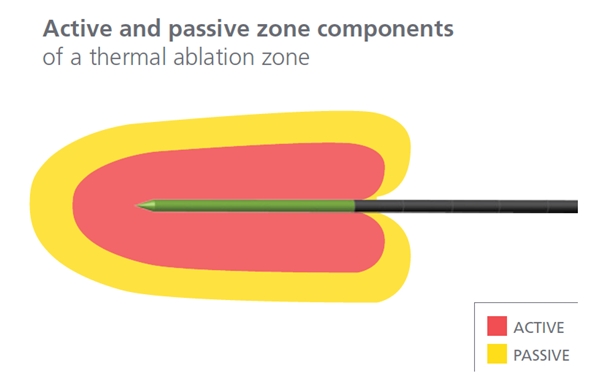
Heat can be conducted away from the tumour by ‘thermal sinks’ such as blood vessels. This affects both microwave and RF technology. There is also an ‘electrical sink’ whereby RF current travels along vessels and other tissue planes ‘short circuiting’ the current and causing unpredictable ablation volumes. Microwave systems are not affected by this.
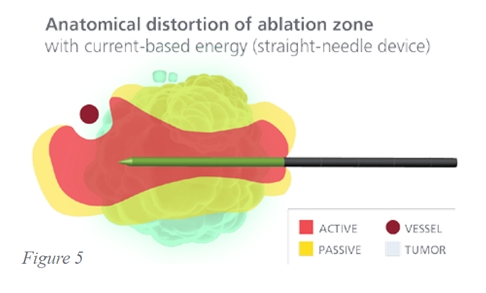
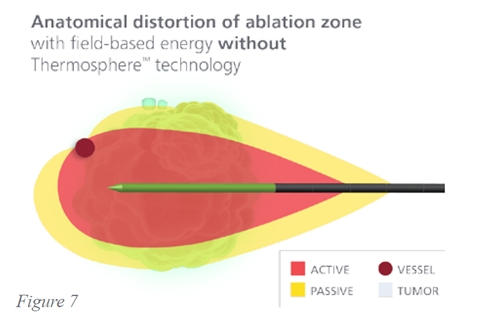
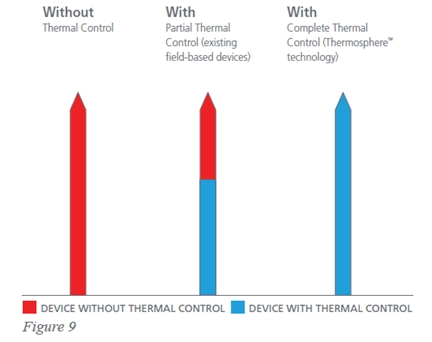
Covidien call their technology ‘Thermosphere technology’. This consists of three components that aim to produce a more spherical and therefore predictable zone of ablation.
These are:
Thermal control
Field control
Wavelength control
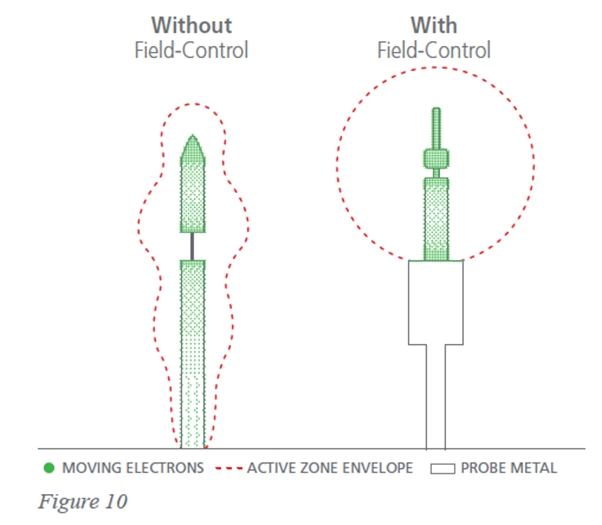
Coaxial waveguides heat up as the microwaves are directed to the probe tip so cooling is needed. Thermal control is cooling of the needle almost all the way to the tip of the device.
Field control restricts the radiating portion of the antenna to the distal end with an RF choke.
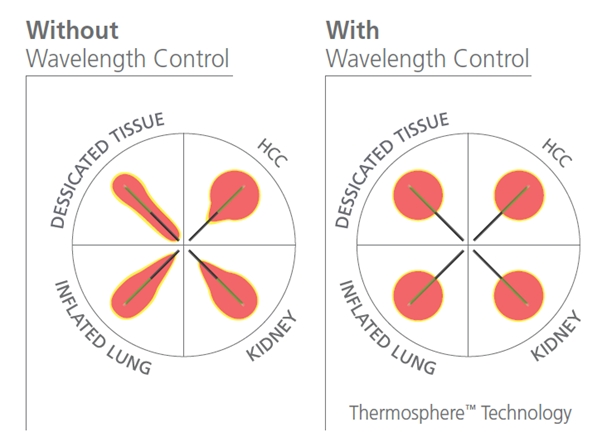
As tissue heats the tissue desiccates. This lowers the dielectric constant. This in turn increases the wavelength. This leads to oval ablation zones. Wavelength control ‘hides’ the radiating metal from the tissue by the circulating fluid. This gives a constant favourable radiating environment.
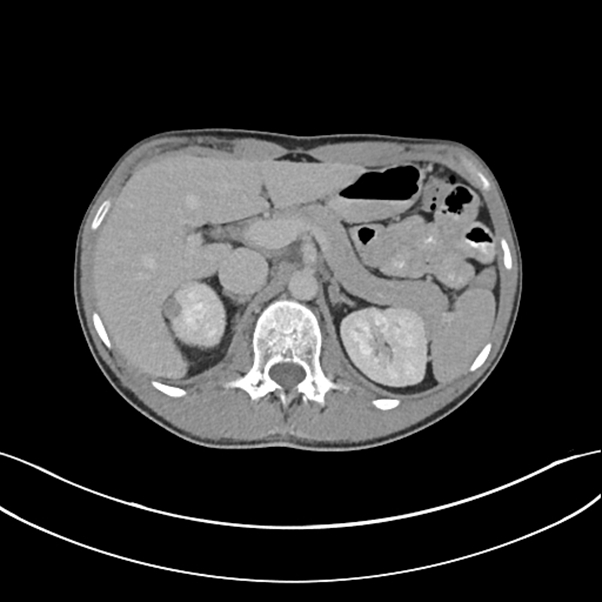
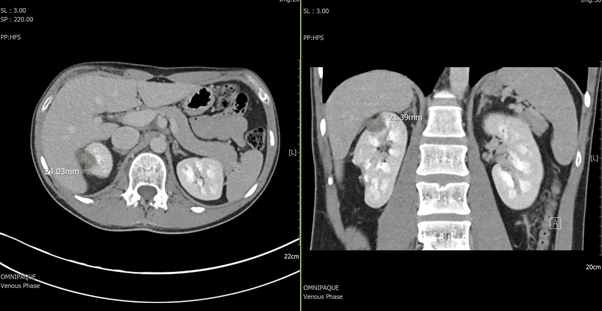
This is a small right upper pole RCC I recently treated using the Emprint system.
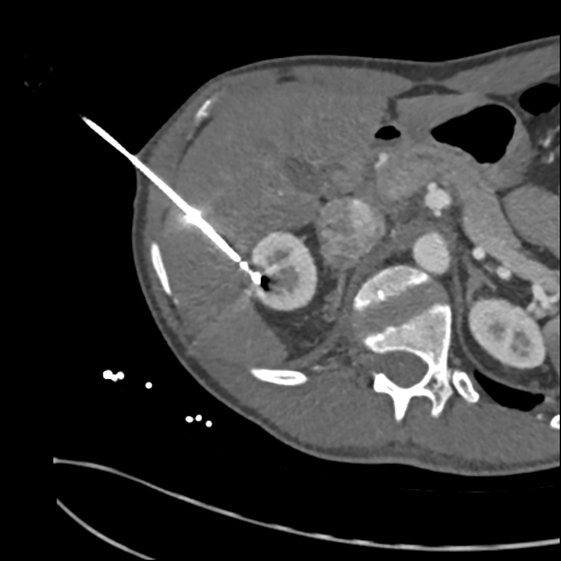
This image shows the microwave needle inserted into the tumour
You can see the relatively rounded ablation zone on the post procedure CT at 3 months.
The other interesting feature of this device is the extreme ease of visibility of the needle/antenna using ultrasound. I think this may be due to the water jacket for cooling.
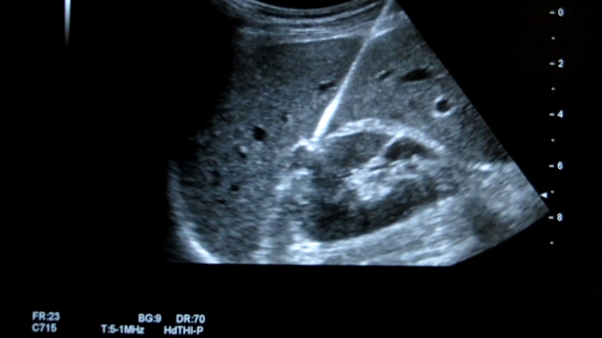
You can see this demonstrated really well in the video tab.
The following 2 pictures show a larger RCC treated using this system.
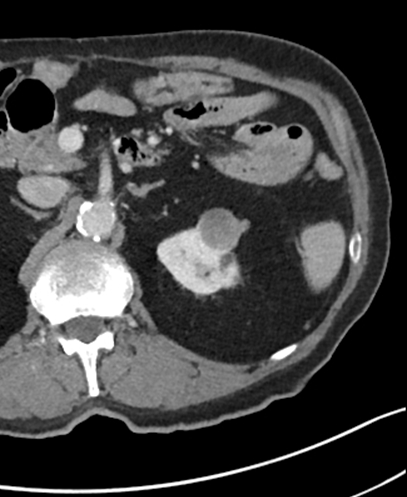
Area of ablation post microwave therapy:
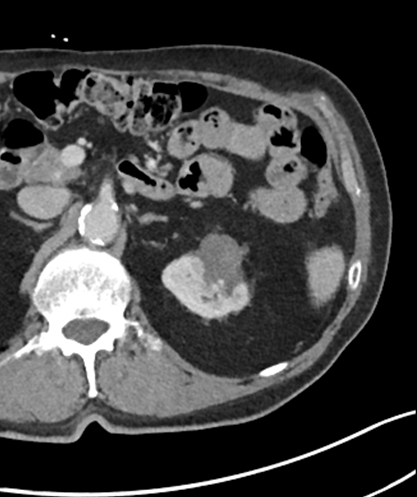
The device itself is extremely easy to use and is well shown in the video tab showing a full microwave ablation.
You insert the needle/antenna into the tumour using US/CT guidance. Then set the time and power for the ablation. You can then perform track ablation by slowly withdrawing the needle whilst active.
The theoretical ablation sizes are in the table below:
This shows the variation with time and power.
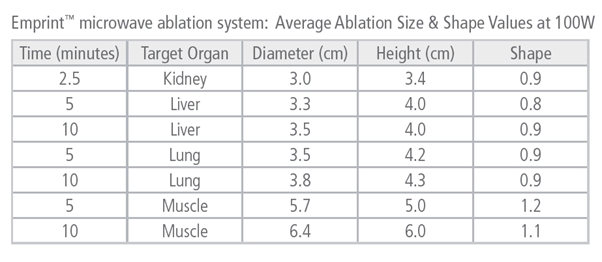
My only slight criticism of the system is the slightly larger needle size compared with RFA, however this is made up for by its visibility and rapid more predicatble ablation zone.
Dr Phil Haslam
Consultant Interventional Radiologist
Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
UK

Did you know you can Register for FREE with this website?
Registration gives you full access to all of the features of WhichMedicalDevice. Find out more ...
WhichMedicalDevice is a FREE resource created by clinicians for clinicians.
Registration is free and gives you unlimited access to all of the content and features of this website.
Find out more...Registration is free and gives you unlimited access to all of the content and features of Which Medical Device. Find out more...
Which Medical Device is a community of clinicians sharing knowledge and experience of the devices and procedures we use on a daily basis. We ask that our members register with us so that we can maintain the unbiased and independent nature of our content. Registration is quick and free.
We do not make your details available to any third parties nor do we send unsolicited emails to our members. You can read our Privacy Policy here.